SWS02 was optimised for sensitive observations of
single lines. It could observe up
to 64 individual small wavelength intervals per spectrum
(each one covering approximately 10 resolution elements, i.e.,
1500-3000 km/s) using the SWS grating mode.
Each range was scanned
back and forth to provide redundancy with minimal scan time of 100
seconds. Dark current measurements were performed before and after
the spectral scan. And a photometric check was
performed at the end, using the internal calibrators. In cases of very
long observations (![]() 3600 sec) there were extra photometric checks.
3600 sec) there were extra photometric checks.
Table 3.2 shows the reset intervals, dwell times, stepsize and number of up-down scans for SWS02. The dwell time may be higher for some merged scans.
| Detector | Reset | Dwell | Stepsize | Number of |
| band | interval | time | LVDT | up-down |
| [s] | [s] | scans | ||
| 1 | 1, 2, 4 | = reset | 1 | n |
| 2,3 | 1, 2 | = reset | 1 | n |
| 4 | 1, 2 | = reset | 2 | n |
Example of an SWS02 observation:
As an example, to observe lines at 10, 12, 35 and 40![]() m the SWS02
carried out the following sequence:
m the SWS02
carried out the following sequence:
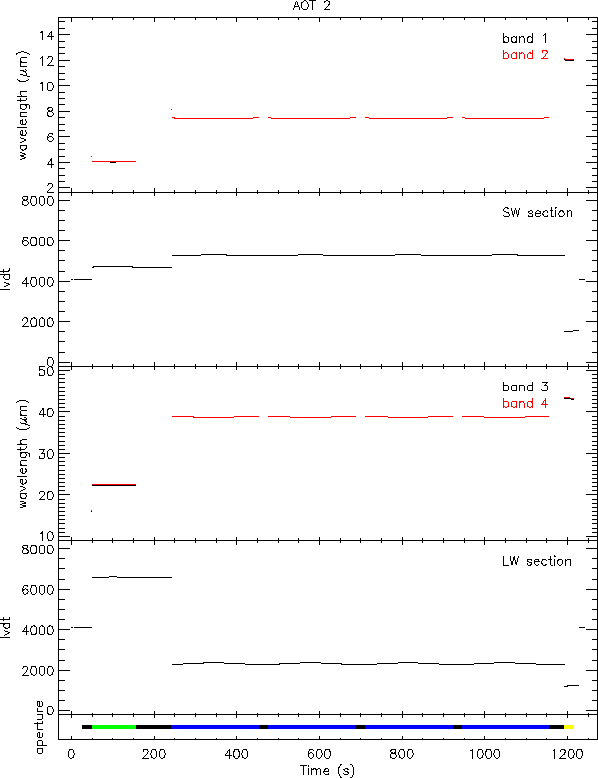
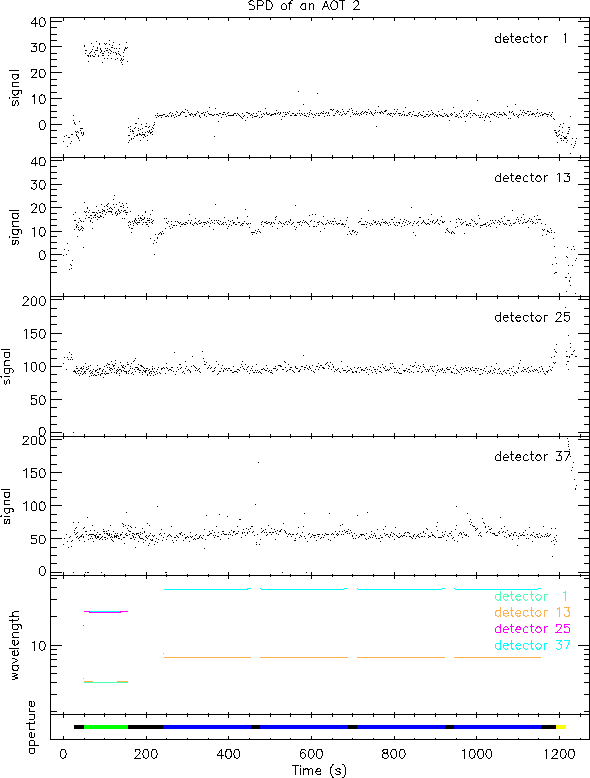
Figure 3.6 shows the wavelength coverage in time of an SWS02. The particular SWS02 is quite a short one, performing only 5 scans. As the individual scans are also short, the up-down character of each of them can hardly be distinguished. Figure 3.7 displays the timeline (SPD) of the first detector in each of the 4 grating bands; not much seems to be happening. Figure 3.8 shows only part of the AAR in the overlap region between band 1D and 2A (upper panel). A faint absorption line is visible in band 1D while it is mostly noise in band 2A. In the lower panel it is shown what can be achieved by post-AAR processing.
|
|