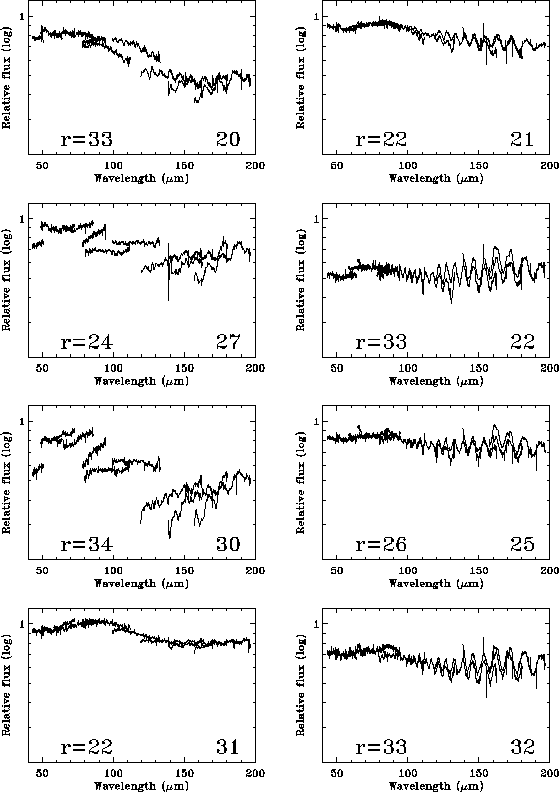
|
For point sources observed off-axis, and to a lesser extent extended
sources, the stitching between adjacent detectors breaks down when the
source lies in a particular part of the beam (see
Figure 6.3). The reason for this is unknown but the
part of the beam affected is the edge that passes close to the cutout in
the contour field mirror, between Mirror 2 and the collimator. At shorter
wavelengths the flux levels are generally higher in this region compared
to similar radii in other parts of the beam, and at longer wavelengths
the effect of fringing is reduced. The spectrum takes on a broken or
fractured appearance with large discontinuities between detectors. The
effect is worse at shorter wavelengths and for the SW detectors it
introduces a strong gradient in the flux with wavelength. The variation
of the mean flux in the fractured region is the main cause of the
asymmetry in the beam, and of the difficulty in modelling it.
Two routines in LIA, CORRECT_SPECTRUM for point sources and
EXTENDED_FLUX
for extended sources, can be applied to reduce this effect in the spectra.

|