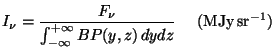 |
(5.3) |
The flux calibration of the SWS instrument has been derived by positioning well known calibration point-like sources at the nominal centre of the instrument beam. The calibration is therefore directly applicable only for point source observations. For extended sources the measured signals have to be converted to surface brightness values rather than flux values.
The derivation of extended source flux from a point source calibration is given by;
where ![]() is the (point source) flux density at the frequency
is the (point source) flux density at the frequency ![]() and
and
![]() is the detector's Beam Profile, normalised to the value at the
position in which the flux calibration has been derived, nominally the (0,0)
position. The variables y and z are angles with respect to the spacecraft
Z and Y axes.
is the detector's Beam Profile, normalised to the value at the
position in which the flux calibration has been derived, nominally the (0,0)
position. The variables y and z are angles with respect to the spacecraft
Z and Y axes.
Table 5.4 lists the conversion factors obtained by integrating the measured SWS beam profiles, according to Equation 5.3. These conversion factors are estimated to be accurate within 10%.