



Next: 8. Getting Started with
Up: 7. Guide to Instrument
Previous: 7.2 Product Files -
Subsections
7.3 Calibration Files
This section gives a description of all the calibration files used during
the automated pipeline processing of LWS data. The contents of these files
are fixed for each version of the processing and can only be updated when a
new OLP version is issued.
The SPD level files are mainly concerned with how LWS output is turned from
engineering units to photocurrent at each grating position and much of this
information has remained unchanged since before launch although parameters
such as discard times have been updated in-orbit. The files LCD2, LCFP and
LCD3 are no longer used.
The Auto-Analysis level files are concerned with the astronomical
calibration of LWS and have evolved with various versions of the LWS
pipeline processing as the understanding of instrument calibration has
improved. In particular the photometric and spectral response calibration of
LWS has changed with each version. The LCTP and LCDK files have only been in
existence since OLP Version 8.
7.3.1 SPD calibration files
The contents and usage of the SPD calibration files have changed as the
pipeline has developed. Some of the calibration files still
read by SPL are no longer used during the processing. Other files
contain information which is no longer used. In the following sections
only the information which is actually used is identified.
Each SPD calibration file contains a version number and date for
identification purposes. The version numbers are contained in the keywords
named XXXXVER, where XXXX is the four letter name of the
calibration file. The date is contained in the keyword LDATE.
The date and version numbers of the calibration files used by Derive-SPD
are written into the header of the SPD and AAR files as a series of
keywords named LSVERSn (n=1,2,...).
7.3.1.1 LCDT: Discard times file
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
- The amount of time to be discarded following each
detector reset, in ms. The LCDT file from OLP Version 7 onwards
effectively contains only a single discard time which
applies to all ramps of all detectors. However, due
to requirements for previous versions of the pipeline, this is
implemented as two separate discard times for each of the ten
detectors. One discard time is for `short' (high signal)
ramps, the other discard time for `long' (low signal) ramps.
Since the introduction of the
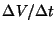 method
of slope fitting in OLP Version 7, all discard times are
set to the same value.
method
of slope fitting in OLP Version 7, all discard times are
set to the same value.
- Two keywords specifying the time period that must be discarded
after a movement of the grating or Fabry-Pérot. These times
are not in use as the amount of time discarded after each
detector reset has been found to be sufficient to cover
mechanism settling times as well.
Table 7.34:
LCDT calibration file keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCDTNSAM |
I |
none |
Threshold for switching from standard set of |
| |
|
|
detector reset discard times to alternate set. |
| LCDTTRTn |
R |
ms |
Standard discard time for detector n (n=0...9) |
| |
|
|
following detector reset. Only used if
number of |
| |
|
|
samples in ramp is less than or equal to
LCDTNSAM. |
| LCDTTRAn |
R |
ms |
Alternate discard time for detector
n (n=0...9) |
| |
|
|
following detector reset. Only used if
number of |
| |
|
|
samples in ramp is greater than to LCDTNSAM. |
- Use:
- To determine how much of every integration ramp has to be
discarded. Used in Derive-SPD processing step `Construct ramps and
discard unusable readouts', see Section 4.3.2.
7.3.1.2 LCAL: Readout limits for the analogue electronics
- Type of File:
- FITS header
- Contents:
-
- Ten values specifying for each detector the minimum
readout value below which the analogue amplification chain does not
respond. All readouts which are below this value are discarded.
See Table 7.35 for the keywords.
- The following ten keywords specify for each detector the maximum
readout value above which the analogue amplification chain saturates.
All readouts above this value are discarded.
See Table 7.35 for the keywords.
Table 7.35:
LCAL calibration file keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCALDMI0 |
I |
- |
Detector SW1 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI1 |
I |
- |
Detector SW2 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI2 |
I |
- |
Detector SW3 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI3 |
I |
- |
Detector SW4 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI4 |
I |
- |
Detector SW5 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI5 |
I |
- |
Detector LW1 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI6 |
I |
- |
Detector LW2 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI7 |
I |
- |
Detector LW3 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI8 |
I |
- |
Detector LW4 minimum readout |
| LCALDMI9 |
I |
- |
Detector LW5 minimum readout |
|
LCALDMX0 |
I |
- |
Detector SW1 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX1 |
I |
- |
Detector SW2 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX2 |
I |
- |
Detector SW3 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX3 |
I |
- |
Detector SW4 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX4 |
I |
- |
Detector SW5 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX5 |
I |
- |
Detector LW1 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX6 |
I |
- |
Detector LW2 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX7 |
I |
- |
Detector LW3 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX8 |
I |
- |
Detector LW4 maximum readout |
| LCALDMX9 |
I |
- |
Detector LW5 maximum readout |
- Use:
- To determine which readouts are outside the limits of the
electronics. Note that this is not the same as the `saturation' limits.
These limits are specified in the LCDB file.
7.3.1.3 LCVC: Detector voltage conversion file
- Type of File:
- FITS header
- Contents:
-
Two keywords are used in the conversion of raw detector
readouts into voltages. The conversion is done using the formula:
V = (raw detector value - LCVCVOFF) * LCVCVFAC
where the keywords are:
LCVCVFAC= Conversion factor, Volts per raw value
LCVCVOFF= Offset to be subtracted from raw value
The conversion factor and the offset value are REAL values.
- Use:
- To convert the readouts into voltages.
7.3.1.4 LCGA: Analogue amplification gains
- Type of File:
- FITS header
- Contents:
-
Eighty keywords (all REAL values) specify the analogue amplification gain
for each gain setting of each detector. Each keyword has the format:
LCGADG<detector><gain>, where <detector> specifies the
detector as a
number between 0 and 9, and <gain> specifies the gain setting
as a
number between 0 and 7.
- Use:
- In Derive-SPD for the conversion of readouts to voltages.
7.3.1.5 LCJF: JF4 amplifier parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
Ten keywords specifying the fixed gain of the JF4 amplifier
for each detector.
Followed by ten keywords specifying the capacitances associated with
each of the JF4 amplifiers.
See Table 7.36 for the keyword names.
Table 7.36:
LCJF calibration file keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCJFJG0 |
R |
- |
Detector SW1 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG1 |
R |
- |
Detector SW2 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG2 |
R |
- |
Detector SW3 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG3 |
R |
- |
Detector SW4 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG4 |
R |
- |
Detector SW5 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG5 |
R |
- |
Detector LW1 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG6 |
R |
- |
Detector LW2 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG7 |
R |
- |
Detector LW3 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG8 |
R |
- |
Detector LW4 JF4 gain |
| LCJFJG9 |
R |
- |
Detector LW5 JF4 gain |
|
LCJFJC0 |
R |
farad |
Detector SW1 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC1 |
R |
farad |
Detector SW2 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC2 |
R |
farad |
Detector SW3 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC3 |
R |
farad |
Detector SW4 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC4 |
R |
farad |
Detector SW5 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC5 |
R |
farad |
Detector LW1 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC6 |
R |
farad |
Detector LW2 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC7 |
R |
farad |
Detector LW3 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC8 |
R |
farad |
Detector LW4 JF4 capacitance |
| LCJFJC9 |
R |
farad |
Detector LW5 JF4 capacitance |
- Use:
- In Derive-SPD for the conversion of readouts to voltages.
7.3.1.6 LCDB: Saturation voltage thresholds for slope fitting
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
This file contains the maximum allowable voltage before a point is regarded
as being saturated. See Section 4.3.4 for a description of how
saturated points are handled.
This file also contains values for the `de-biasing' parameters and the
thresholds for switching between first and second order slope fitting.
These values have not been used since the introduction of the
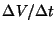 method of slope fitting in OLP Version 7.
method of slope fitting in OLP Version 7.
Table 7.37:
LCDB calibration file keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCDBVM0 |
R |
Volts |
Detector SW1 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM1 |
R |
Volts |
Detector SW2 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM2 |
R |
Volts |
Detector SW3 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM3 |
R |
Volts |
Detector SW4 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM4 |
R |
Volts |
Detector SW5 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM5 |
R |
Volts |
Detector LW1 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM6 |
R |
Volts |
Detector LW2 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM7 |
R |
Volts |
Detector LW3 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM8 |
R |
Volts |
Detector LW4 maximum readout |
| LCDBVM9 |
R |
Volts |
Detector LW5 maximum readout |
- Use:
- In Derive-SPD for identifying saturated points.
7.3.1.7 LCD1: First level deglitching parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
See Table 7.38 for the contents of this file.
Table 7.38:
LCD1 calibration file keywords.
| name |
type |
unit |
description |
| LCD1GFRA |
R |
none |
Glitches whose height is below this fraction of |
|
|
|
|
the ramp height will be rejected |
|
LCD1SPRA |
R |
none |
`Spikes' whose height is below this fraction of |
|
|
|
|
the ramp height will be rejected |
|
LCD1SDRJ |
R |
none |
Number of standard deviations from mean for point |
|
|
|
|
to be marked as an outlier. |
|
LCD1PGRJ |
I |
none |
Number of ramps to discard after a
positive glitch. |
|
LCD1NGRJ |
I |
none |
Number of ramps to discard after a
negative glitch. |
|
LCD1GRRJ |
L |
none |
Indicates if the whole of the glitched ramp should |
|
|
|
|
be discarded. |
|
LCD1PGRI |
I |
none |
For illuminator flashes, the number of ramps to |
|
|
|
|
discard after a positive glitch. |
|
LCD1NGRI |
I |
none |
For illuminator flashes, the number of ramps to |
|
|
|
|
discard after a negative glitch. |
|
LCD1GRRJ |
L |
none |
For illuminator flashes, indicates if the whole of |
|
|
|
|
the glitched ramp should be discarded. |
- Use:
- Contains various parameters which control the detection and
removal of glitched points by first level deglitching.
7.3.1.8 LCGH: Glitch History file parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
The first keyword (LCGHGHMR)
gives the maximum number of records that can be written to the LWS
Glitch History file. This was introduced because of early fears
that this file might grow uncontrollably. In fact this has not proved
to be the case and this value is set to a high enough value to
cope with all observations.
Table 7.39:
LCGH calibration file keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCGHGHMR |
I |
- |
Maximum number of records |
- Use:
- For writing data to the LWS Glitch History file.
7.3.1.9 LCD2: Second level deglitching parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
This file relates to a deglitching stage used during early versions of the
pipeline. This file is still currently read by SPL, but its contents are
not used.
- Use:
- Not used
7.3.1.10 LCFP: Parameters for electronic filters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
Ten keywords containing the time constants for the high pass
filter for each detector. The times are specified in seconds.
These values have not been used since the introduction
of the
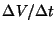 method of slope fitting in OLP
Version 7.
method of slope fitting in OLP
Version 7.
- Use:
- Not used
7.3.1.11 LCD3: Third level deglitching parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
This file relates to a deglitching stage used during early versions of the
pipeline. This file is still currently read by SPL, but its contents are
not used.
- Use:
- Not used
7.3.2 Auto-Analysis calibration files
All Auto-Analysis calibration files contain a set of standard keywords in
their header to identify the version and validity of the file.
These keywords can be used to check that the calibration files are valid
for the data that is being processed. The keywords are checked during the
automatic processing of the data in the OLP pipeline.
The keywords can be found in Table 7.40
Table 7.40:
Auto-Analysis calibration files general keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LDATE |
C |
- |
date of creation or update |
| LVER |
I |
- |
version number |
| LMODEL |
C |
- |
identifies instrument model (always FM) |
| LVLSTART |
I |
- |
UTK of start of validity |
| LVLEND |
I |
- |
UTK of end of validity |
| LVLBIAn |
I |
- |
indicates the bias level for which |
| |
|
|
the file is valid for each detector |
| |
|
|
(0-9). If LVLBIA0 is set to  1 1 |
| |
|
|
file is independent of bias, other |
| |
|
|
bias levels are then not present |
The version number and date of all the calibration files used by Auto-Analysis
are written into the header of the LSAN file as a series of keywords named
LVERSn (n=1,2,...).
7.3.2.2 LCIR: Illuminator reference file
- Type of File:
- FITS binary table
- Contents:
-
The LCIR file is a calibration file which contains a reference
photocurrent value for each ramp in an illuminator flash for each
detector. The LCIR is a FITS binary table extension file of shape 1,
i.e. there is only one LCIR file which covers the whole mission.
The file contains an illuminator `type' number as part of each record,
allowing it to contain reference data for more than one `type'
of illuminator flash. The comments in the LCIR file header should
describe each flash type stored in the file.
For each flash type the LCIR file contains only the data starting from
when the first illuminator was switched on and ending when the last
illuminator was switched off. The background measurements
at the beginning and end of the
flash are not contained in the LCIR file. The the reference photocurrent
values in the LCIR file have had the background photocurrent already
subtracted.
Each LCIR record contains a status flag which allows selected points to be
ignored when ratioing against the flash data. This can be used to mask out
data
from illuminator levels which do not provide useful data. Any photocurrent
value in the LCIR file which is set to zero will also be ignored in the
same
way. Values may be zero because of glitches in the reference data.
The header of the LCIR file contains keywords which specify NSD, the number
of standard deviations for median clipping the data. These keywords are:
LCIRNSDB (Number of Standard deviations to use for median clipping of
background) and LCIRNSDF (Number of Standard deviations to user for median
clipping of flash data).
The record structures is given in Table 7.41
Table 7.41:
LCIR calibration file record structure.
|
name |
offset |
Number |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCIRTYPE |
0 |
1 |
I*4 |
- |
Number identifying type of |
| |
|
|
|
|
illuminator flash |
| LCIRPHC |
4 |
10 |
R*4 |
A |
Reference photocurrent, |
| |
|
|
|
|
with background subtracted |
| LCIRPHCU |
44 |
10 |
R*4 |
A |
Uncertainty in reference |
| |
|
|
|
|
photocurrent |
| LCIRSTAT |
84 |
1 |
I*4 |
- |
Status word. 1=use this value; |
| |
|
|
|
|
0=ignore this value |
| LCIRICS |
88 |
1 |
I*4 |
- |
Illuminator commanded status |
- Use:
- For the flux calibration of the data.
7.3.2.3 LCGW: Grating position to wavelength conversion parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS binary table.
- Contents:
-
This file contains the parameters required for converting the grating LVDT
readout values into wavelength. Since the wavelength calibration changes
over time this file contains different sets of coefficients for different
time periods. Each record of the LCGW file contains one set of
coefficients,
which are valid for a particular time period. Rather than use a time key
directly, the LCGW file uses the revolution number to identify which record
is valid for which time period. Each record contains the start and end
revolution numbers for which it is valid.
The record structure of the LCGW file is shown in
Table 7.42.
The header of the LCGW file also contains keywords which contain fixed
values for use in the conversion. These keywords are shown in
Table 7.43.
Table 7.42:
LCGW calibration file record structure.
|
name |
Offset |
number |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCGWSREV |
0 |
1 |
I*4 |
- |
Revolution number of start |
| |
|
|
|
|
of validity for this record |
| LCGWEREV |
4 |
1 |
I*4 |
- |
Revolution number of end of |
| |
|
|
|
|
validity for this record |
| LCGWCOEF |
8 |
5 |
R*4 |
- |
Conversion coefficients |
| LCGWADET |
28 |
10 |
R*4 |
deg |
Angle for each detector |
Table 7.43:
LCGW keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCGWLINE |
R |
- |
Number of lines per 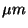 on grating on grating |
| LCGWOdet |
I |
- |
Order number for each detector |
| |
|
|
(det=`SW1'...`LW5') |
- Use:
- Wavelength calibration of the grating.
7.3.2.4 LCGR: Grating relative response file
- Type of File:
- FITS primary array
- Contents:
-
This FITS file contains the grating relative wavelength
responsivities for each detector at selected wavelengths. The
file applies for a particular bias level. The data are normalised to
the wavelength at which the absolute responsivity is measured.
The relative responsivity includes a correction for the aperture
size of the instrument, assuming the source is a point source in
the centre of the beam. The unit of the relative responsivity
therefore is cm
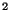 .
The file is written as a FITS primary array with three axis
(NAXIS=3). The axis are defined as given in
Table 7.44.
.
The file is written as a FITS primary array with three axis
(NAXIS=3). The axis are defined as given in
Table 7.44.
Table 7.44:
LCGR calibration file structure.
|
name |
Number of |
type |
unit |
description |
| |
elements |
|
|
|
|
NAXIS1 |
4 |
R*4 |
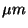 |
Wavelength |
| |
|
R*4 |
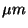 |
Uncertainty in wavelength |
| |
|
R*4 |
cm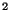 |
Relative Responsivity |
| |
|
R*4 |
cm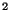 |
Uncertainty in responsivity |
| NAXIS2 |
10 |
R*4 |
- |
Detector number |
| NAXIS3 |
4096 |
R*4 |
- |
Grating LVDT value |
The header of the file contains keywords which specify the range of grating
positions which are used within the file and the `nominal' wavelength
range for
each detector. The nominal range is where the calibration is of acceptable
quality. Everything outside the nominal range has poor calibration and is
flagged with a warning flag in the LSAN status word. These keywords are shown
in Table 7.45.
Table 7.45:
LCGR keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LSTARPOS |
I |
- |
First valid grating position in file |
| LENDPOS |
I |
- |
Last valid grating position in file |
| LSTRNOMn |
R |
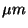 |
Start of nominal wavelength range |
| |
|
|
for detector n (n=0...9) |
| LENDNOMn |
R |
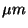 |
End of nominal wavelength range |
| |
|
|
for detector n (n=0...9) |
- Use:
- Relative responsivity correction for grating mode.
7.3.2.5 LCFW: Fabry-Pérot wavelength calibration parameters
- Type of File:
- FITS Header
- Contents:
-
This FITS file contains the parameters required for converting FP
position into wavelength.
The parameters are the coefficients for the third order polynomial
that is used to describe the dependence of the wavelength on the
position of the FP etalons. Because of the precision of the FP
wavelength calibration, these values should be read into real*8
variables.
Table 7.46 gives the keywords for this file.
Table 7.46:
LCFW calibration file keywords.
|
name |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCFWFLC0 |
D |
- |
FPL zeroth order coefficient |
| LCFWFLC1 |
D |
- |
FPL first order coefficient |
| LCFWFLC2 |
D |
- |
FPL second order coefficient |
| LCFWFLC3 |
D |
- |
FPL third order coefficient |
| LCFWFSC0 |
D |
- |
FPS zeroth order coefficient |
| LCFWFSC1 |
D |
- |
FPS first order coefficient |
| LCFWFSC2 |
D |
- |
FPS second order coefficient |
| LCFWFSC3 |
D |
- |
FPS third order coefficient |
- Use:
- Wavelength calibration of Fabry-Pérot data.
7.3.2.6 LCGB: Grating spectral bandwidth correction factors
- Type of file:
- FITS binary table
- Contents:
- The correction factor for the grating spectral
bandwidth for each of the ten LWS detectors. For each detector the
factor and its uncertainty is given. The record structure can be found
in Table 7.47.
Table 7.47:
LCGB calibration file record structure.
|
name |
offset |
number |
type |
unit |
description |
|
LCGBDET |
0 |
1 |
C*3 |
- |
Detector |
| LCGBSPAR |
3 |
1 |
I*1 |
- |
Filler |
| LCGBSB |
4 |
1 |
R*4 |
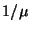 m m |
Bandwidth |
| LCGBSBU |
8 |
1 |
R*4 |
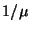 m m |
Uncertainty in bandwidth |
- Use:
- In Auto-Analysis to correct fluxes for the spectral bandwidth
for grating spectra.
7.3.2.7 LCDK: Fixed dark current calibration file
- Type of file:
- binary extension FITS file
- Contents:
- The file contains the dark current values for
each detector.
7.3.2.8 LCTP: Fabry-Pérot throughput correction calibration file
- Type of file:
- FITS header
- Contents:
- The file contains the coefficients of the
polynomial fits of
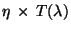 (product of the transmission efficiency
(product of the transmission efficiency
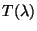 and the effective
spectral element width
and the effective
spectral element width 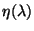 ) for FPS
and the two sections of FPL (SW4-LW1 and LW2-LW5)
) for FPS
and the two sections of FPL (SW4-LW1 and LW2-LW5)




Next: 8. Getting Started with
Up: 7. Guide to Instrument
Previous: 7.2 Product Files -
ISO Handbook Volume III (LWS), Version 2.1, SAI/1999-057/Dc
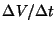 method
of slope fitting in OLP Version 7, all discard times are
set to the same value.
method
of slope fitting in OLP Version 7, all discard times are
set to the same value.